Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control
Division of Air Quality
PROPOSED
REGISTER NOTICE
SAN#: 2013-14
1. TITLE OF REGULATIONS:
Revision to 7 DE Admin. Code 1103, Ambient Air Quality Standards.
2. BRIEF SYNOPSIS OF THE SUBJECT, SUBSTANCE AND ISSUES:
This revision to 7 DE Admin. Code 1103 was identified in an April 1, 2013 Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Controls (DNREC) report titled, "Executive Order 36 Report to The Office of the Governor." Revisions are proposed to bring the regulatory standards up-to-date with current federal requirements. 1103 currently contains outdated test methods and emission standards. This requires citizens and industry to review both state regulations and federal regulations, and to reconcile the two, in order to understand the requirements that apply in Delaware. This could also lead to state and federal requirements being incorrectly applied. This unnecessary regulatory burden will be eliminated with this revision to 1103. The revised regulation will also be submitted to the EPA as a revision to Delaware's State Implementation Plan (SIP).
3. POSSIBLE TERMS OF THE AGENCY ACTION:
None
4. STATUTORY BASIS OR LEGAL AUTHORITY TO ACT:
7 Delaware Code, Chapter 60, Environmental Control
5. OTHER REGULATIONS THAT MAY BE AFFECTED BY THE PROPOSAL:
None
6. NOTICE OF PUBLIC COMMENT:
Interested parties may submit comments in writing to Ron Amirikian, Division of Air Quality, Blue Hen Corporate Center, 655 S. Bay Road, Suite 5N, Dover, DE 19901, and/or statements and testimony may be presented either orally or in writing at the public hearing to be held on Thursday, August 1, 2013, beginning at 6:00 p.m. in DNREC's Richards and Robbins Building auditorium, 89 Kings Hwy, Dover, Delaware 19901.
7. PREPARED BY:
Ron Amirikian (302) 739-9402 June 12, 2013 Email address: ronald.amirikian@state.de.us
1103 Ambient Air Quality Standards
09/11/99 (Insert Revision Effective Date)
1.1 Air quality standards are required to assure that ambient air quality shall be consistent with established criteria and shall serve to effectively and reasonably manage the air resources of the State of Delaware.
1.1.1 Primary air quality standards provide public health protection, including protecting the health of sensitive populations such as asthmatics, children, and the elderly.
1.1.2 Secondary air quality standards provide public welfare protection, including protection against decreased visibility and damage to crops, animals, vegetation, and buildings.
1.2 At such time as additional pertinent information becomes available with respect to applicable air quality criteria, recommendations shall be incorporated and the air quality standards shall be subject to revisions.
1.3 The absence of a specific ambient air quality standard shall not preclude actions by the Department to control contaminants to assure protection, safety, welfare, and comfort of the people of the State of Delaware.
1.4 Air quality standards are defined by frequency distribution presentations and arithmetic averages. The characteristic parameters describing the frequency distribution are the geometric mean and 99th percentile.
1.4.1 The geometric mean is defined as the Nth root of the product of N numbers. Assuming a log???normal cumulative frequency distribution, the 50th percentile value will be equal to the geometric mean.
1.4.2 The arithmetic average mean is defined as the sum of a set of values divided by the number of values.
1.4.3 The 99th percentile for a group of numbers is defined as that value which is exceeded by one percent of the numbers.
1.5 The ambient air quality values stated herein shall apply to all areas outside a source property line.
1.6 The sampling and analytical procedures and techniques employed to determine ambient air concentrations of contaminants shall be consistent with methods which result in a representative evaluation of the prevailing conditions. The following methods shall be used directly or employed as reference standards against which other methods may be calibrated;
1.6.1 Ambient concentrations of total suspended particulates shall be determined by the reference high volume method in accordance with 40 CFR, Part 50, Appendix B, June 29, 1979 Appendix B, Reference Method for the Determination of Suspended Particulate Matter in the Atmosphere (High-Volume Method), April 22, 1983.
1.6.2 Ambient concentrations of sulfur dioxide shall be determined by the reference or equivalent method in accordance with 40 CFR, Part 50, Appendix A-1, June 29, 1979. Reference Method Principle and Calibration Procedure for the Measurement of Sulfur Dioxide in the Atmosphere (Ultraviolet Fluorescence Method), June 22, 2010, or 40 CFR, Part 50, Appendix A-2, Reference Method for the Measurement of Sulfur Dioxide in the Atmosphere (Pararosaniline Method), June 22, 2010.
1.6.3 Ambient concentrations of carbon monoxide shall be determined by the reference method in accordance with 40 CFR, Part 50, Appendix C, June 29, 1979. Measurement Principle and Calibration Procedure for the Measurement of Carbone Monoxide in the Atmosphere (Non-Dispersive Infrared Photometry, August 31, 2011.
1.6.4 Ambient concentrations of ozone corrected for interferences due to nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide shall be determined by the reference method in accordance with 40 CFR, Part 50, Appendix D, June 29, 1979. Measurement Principle and Calibration Procedure for the Measurement of Ozone in the Atmosphere, July 18, 1997.
1.6.5 Ambient concentrations of methane and non???methane hydrocarbons shall be determined by the reference method in accordance with 40 CFR, Part 50, Appendix E, June 29, 1979.
1.6.6 Ambient concentrations of nitrogen dioxide shall be determined by the reference method in accordance with 40 CFR, Part 50, Appendix F, June 29, 1979. Measurement Principle and Calibration Procedure for the Measurement of Nitrogen Dioxide in the Atmosphere (Gas Phase Chemiluminescence), January 20, 1983.
1.6.7 Ambient concentrations of hydrogen sulfide shall be determined by gas chromatographic separation - flame photometric detection.
1.6.8 Ambient concentrations of lead shall be determined by the reference method in accordance with 40 CFR, Part 50, Appendix G, June 29, 1979. Reference Method for the Determination of Lead in Suspended Particulate Matter Collected from Ambient Air, November 12, 2008.
1.6.9 Ambient concentrations of PM10 particulate shall be determined by a reference method in accordance with 40 CFR, Part 50, Appendix J, Reference Method for the Determination of Particulate Matter as PM10 in the Atmosphere, August 7, 1987, or an equivalent method.
1.6.10 Ambient concentrations of PM2.5 particulate shall be determined by the reference method based on 40 CFR, Part 50, Appendix L, as found in the Federal Register dated July 18, 1997, on page 38714 - 38752. Reference Method for the Determination of Fine Particulate Matter as PM2.5 in the Atmosphere, October 17, 2006.
1.7 Air quality standards are expressed in metric units with the approximate equivalent volumetric units in parentheses. The standard conditions for air ambient monitoring is 760 mm. Hg and 25oC. The formula to convert metric units to parts per million (ppm) is:
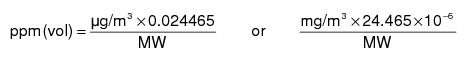
where MW is molecular weight of the contaminant being measured.
02/01/1981
No person shall cause the air quality standards specified in this Regulation to be exceeded.
02/01/1981
3.1 The Primary Ambient Air Quality Standards for Particulate Matter are:
3.1.1 An annual geometric mean of 75 micrograms per cubic meter not to be exceeded, based upon 24 hour average concentrations.
3.1.2 A value of 260 micrograms per cubic meter not to be exceeded more than once per year, based upon 24 hour average concentrations.
3.2 The Secondary Ambient Air Quality Standards for Particulate Matter are:
3.2.1 An annual geometric mean of 60 micrograms per cubic meter as a guideline for achieving the secondary standard based upon 24 hour average concentrations.
3.2.2 A value of 150 micrograms per cubic meter not to be exceeded more than once per year, based upon 24 hour average concentrations.
02/01/1981 (Insert Revision Effective Date)
4.1 The Primary Ambient Air Quality Standards for Sulfur Oxides measured as Sulfur Dioxide are as follows:
4.1.1 An annual arithmetic average value of 80 ??g/m3, (0.03 ppm) not to be exceeded, based upon 24 hour average concentrations. The national primary 1-hour air quality standard for oxides of sulfur is 75 parts per billion (ppb) measured in the ambient air as sulfur dioxide. The 1-hour ambient air quality standard is when the three-hour average of the annual (99th percentile) of the daily maximum 1-hour average concentration is less than or equal to 75 ppb.
4.1.1 Compliance with the national primary 1-hour air quality standard is determined in accordance with 40 CFR Part 50 Appendix T, Interpretation of the Primary National Ambient Air Quality Standards for Oxides of Sulfur (Sulfur Dioxide), June 23, 2010.
4.1.2 A twenty???four average value of 365 ??g/m3 (0.14 ppm) not to be exceeded more than once per year based upon 24 hour average concentrations. The national primary 1-hour air quality standard for oxides of sulfur is set forth in 40 CFR Part 50.17, National Primary Ambient Air Quality Standards for Sulfur Oxides (Sulfur Dioxide), June 22, 2010.
4.2 The Secondary Ambient Air Quality Standards for Sulfur Oxides measured as Sulfur Dioxide are as follows:
4.2.1 A three???hour average value of 1300 micrograms per cubic meter (0.5 ppm), not to be exceeded more than once per year.
4.2 The 24-hour primary national ambient air quality standard for oxides of sulfur is 0.14 parts per million (ppm), not to be exceeded more than once per calendar year.
4.2.1 Compliance with the national 24-hour primary ambient air quality standard for oxides of sulfur is determined in accordance with 40 CFR Part 50, Appendix A-1, Reference Method Principle and Calibration Procedure for the Measurement of Sulfur Dioxide in the Atmosphere (Ultraviolet Fluorescence Method), June 22, 2010, or 40 CFR, Part 50, Appendix A-2, Reference Method for the Measurement of Sulfur Dioxide in the Atmosphere (Pararosaniline Method), June 22, 2010.
4.2.2 The national primary 24-hour ambient air quality standard for sulfur oxides is set forth in 40 CFR Part 50.4, National Primary Ambient Air Quality Standards for Sulfur Oxides (Sulfur Dioxide), June 22, 2010.
4.3 The national primary annual ambient air quality standard for sulfur oxides of 0.030 parts per million (ppm), annual arithmetic mean, shall not be exceeded.
4.3.1 Compliance with the national annual primary ambient air quality standard for oxides of sulfur is determined in accordance with 40 CFR Part 50, Appendix A-1, Reference Method Principle and Calibration Procedure for the Measurement of Sulfur Dioxide in the Atmosphere (Ultraviolet Fluorescence Method), June 22, 2010, or 40 CFR, Part 50, Appendix A-2, Reference Method for the Measurement of Sulfur Dioxide in the Atmosphere (Pararosaniline Method), June 22, 2010.
4.3.2 The national primary 24-hour ambient air quality standard for sulfur oxides is set forth in 40 CFR Part 50.4, National Primary Ambient Air Quality Standards for Sulfur Oxides (Sulfur Dioxide), June 22, 2010.
4.4 The national secondary 3-hour ambient air quality standard for sulfur oxides is 0.5 parts per million (ppm), not to be exceeded more than once per calendar year.
4.4.1 Compliance with the national secondary 3-hour ambient air quality standard for oxides of sulfur is determined in accordance with 40 CFR Part 50, Appendix A-1, Reference Method Principle and Calibration Procedure for the Measurement of Sulfur Dioxide in the Atmosphere (Ultraviolet Fluorescence Method), June 22, 2010, or 40 CFR, Part 50, Appendix A-2, Reference Method for the Measurement of Sulfur Dioxide in the Atmosphere (Pararosaniline Method), June 22, 2010.
4.4.2 The national secondary 3-hour ambient air quality standard for sulfur oxides is set forth in 40 CFR Part 50.5, National Secondary Ambient Air Quality Standard for Sulfur Oxides (Sulfur Dioxide), May 22, 1996.
02/01/1981
5.1 The average concentration of carbon monoxide taken over any consecutive eight hours shall not exceed a value of 10 milligrams per cubic meter (9 ppm) more than once per year.
5.2 The average concentration of carbon monoxide taken over any one hour period shall not exceed 40 milligrams per cubic meter (35 ppm) more than once per year.
09/11/1999 (Insert Revision Effective Date)
6.1 One-hour primary and secondary ambient air quality standards for ozone
The average number of days per calendar year with a maximum one hour average value exceeding 235 ??g/m3 (0.12 ppm) shall be equal to or less than one, averaged over three consecutive years. This standard shall be applicable to New Castle County and Kent County. The 1-hour primary and secondary ambient air quality standard for ozone is 235 ??g/m3 (0.12 ppm). The primary and secondary ozone ambient air quality standards are met when the number of days per calendar year with maximum hourly average concentrations above 235 ??g/m3 (0.12 ppm is equal to or less than 1, as determined by 40 CFR Part 50, Appendix H, Interpretation of the 1-hour Primary and Secondary National Ambient Air Quality Standards for Ozone, July 18, 1997. The 1-hour primary and secondary national ambient air quality standards are set forth in 40 CFR Part 50.9, National 1-hour Primary and Secondary Ambient Air Quality Standards for Ozone, May 14, 2012.
6.2 Eight-hour primary and secondary ambient air quality standards for ozone
The average of the fourth highest daily maximum eight-hour average ozone concentration is less than or equal to 0.08 ppm, averaged over three consecutive years. This standard applies to all Counties in Delaware. The 8-hour primary and secondary ambient air quality standard for ozone is 0.075 parts per million (ppm). The primary and secondary ozone ambient air quality standards are met when the 3-year average of the annual fourth-highest daily maximum 8-hour average ozone concentration is less than or equal to 0.075 ppb, as determined in accordance with 40 CFR Part 50, Appendix P, Interpretation of the Primary and Secondary Air quality Standards for Ozone, May 27, 2008. The 8-hour primary and secondary ozone standards are set forth in 40 CFR Part 50.15, National Primary and Secondary Air Standards for Ozone, May 27, 2008.
02/01/1981
7.1 The hydrocarbons standard in 7.2 of this regulation is for use as a guide in devising implementation plans to achieve the ozone standard.
7.2 The average concentration of hydrocarbons, exclusive of methane, taken over a three hour period from 6 to 9 a.m., local time, shall not exceed 160 micrograms per cubic meter (0.24 ppm) more than once per year.
02/01/1981 (Insert Revision Effective Date)
The annual arithmetic mean concentration of nitrogen dioxide shall not exceed 100 micrograms per cubic meter (0.05 ppm).
8.1 The national primary and secondary air quality standards for oxides of nitrogen (nitrogen dioxide indicator) are as follows:
8.1.1 The primary 1-hour air quality standard for oxides of nitrogen is 100 parts per billion (ppb), 1-hour average concentration, measured in the ambient air as nitrogen dioxide. Compliance with the 1-hour standard is demonstrated when the three-year average of the 98th percentile of the daily maximum 1-hour average concentration is less than or equal to 100 ppb, as determined with 40 CFR Part 50, Appendix S, Interpretation of the Primary Air Quality Standards for Oxides of Nitrogen (Nitrogen Dioxide), February 9, 2010.
8.1.2 The primary annual air quality standard for oxides of nitrogen is 53 parts per billion (ppb), annual average concentration, measured in the ambient air as nitrogen dioxide. The primary annual air quality standard is demonstrated when the average annual concentration in a calendar year is less than or equal to 53 ppb, as determined with 40 CFR Part 50, Appendix S, Interpretation of the Primary Air Quality Standards for Oxides of Nitrogen (Nitrogen Dioxide), February 9, 2010.
8.1.3 The secondary annual air quality standard for oxides of nitrogen is 53 parts per billion (ppb), annual arithmetic mean concentration, measured in the ambient air as nitrogen dioxide. The secondary ambient air quality standard is demonstrated when the annual arithmetic mean concentration in a calendar year is less than or equal to 0.053 ppm. To demonstrate attainment, an annual mean must be based upon hourly data that are at least 75 percent complete or upon data derived from manual methods that are at least 75 percent complete for the scheduled sampling days in each calendar quarter.
8.2 The primary and secondary air quality standards for nitrogen dioxide are as set forth in 40 CFR Part 50.11, February 9, 2010.
02/01/1981
9.1 The average concentration of hydrogen sulfide taken over any consecutive three minutes shall not exceed 0.06 ppm.
9.2 The average concentration of hydrogen sulfide taken over any consecutive 60 minutes shall not exceed 0.03 ppm.
02/01/1981 (Insert Revision Effective Date)
The 24 hour concentration of lead averaged over a calendar quarter shall not exceed 1.5 micrograms per cubic meter. The national primary and secondary ambient air quality standard for lead (Pb) and its compounds are 0.15 micrograms per cubic meter (??g/m3), arithmetic mean concentration over a 3-month period measured in the ambient air as Pb. The national primary and secondary air quality standards are set forth in 40 CFR Part 50.16, National Primary and Secondary Ambient Air Quality Standards for Lead November 12, 2008.
02/11/2003 (Insert Revision Effective Date)
11.1 The Primary and Secondary Ambient Air Quality Standards for Particulate Matter, measured as PM10 are:
11.1.1 The primary and secondary air quality standards for PM10 are 150 micrograms per cubic meter (??g/m3), 24 hour average concentration. The standards are attained when the expected number of days per calendar year with a 24-hour average concentration above 150 ??g/m3, as determined in accordance with 40 CFR, Part 50, Appendix K, Interpretation of the National Ambient Air Quality Standards for Particulate Matter, October 17, 2006, is equal to or less than one. The national primary and secondary air quality standards are set forth in 40 CFR Part 50.6, National Primary and Secondary Ambient Air Quality Standards for PM10.
11.1.2 50 micrograms per cubic meter (??g/m3), annual arithmetic mean. The standards are attained when the expected annual arithmetic mean concentration, as determined in accordance with 40 CFR, Part 50, Appendix K, , is less than or equal to 50 ??g/m3. Reserved
11.2 The Primary and Secondary Ambient Air Quality Standards for Particulate Matter, measured as PM2.5 are:
11.2.1 65 The 24-hour primary and secondary air quality standard is 35 micrograms per cubic meter (F??g/m3), 24-hour average concentration. The 24-hour primary and secondary PM2.5 standards are met when the 98th percentile 24-hour concentration, as determined in accordance with 40 CFR, Part 50, Appendix N, as found in the Federal Register dated July 18, 1997, on page 38757 - 38758, Interpretation of the National Ambient Air Quality Standards for PM2.5, January 15, 2013, is less than or equal to 65 35 ??g/m3. The national 24-hour hour primary and secondary air quality standards are set forth in 40 CFR Part 50.13, National Primary and Secondary Air Quality Standards for PM2.5, October 17, 2006.
11.2.2 15.0 The primary annual air quality standard is 12.0 micrograms per cubic meter (mg/m3) annual arithmetic mean concentration. The annual primary and secondary PM2.5 standards are met when the annual arithmetic mean concentration, as determined in accordance with 40 CFR, Part 50, Appendix N, as found in the Federal Register dated July 18, 1997, on page 38756 - 38757 Interpretation of the National Ambient Air Quality Standards for PM2.5, January 15, 2013, is less than or equal to 152.0 ??g/m3. The national annual primary and secondary air quality standards are set forth in 40 CFR Part 50.18, National Primary and Secondary Air Quality Standards for PM2.5, January 15, 2013.
11.2.3 The secondary annual air quality standard is 15.0 micrograms per cubic meter (??g/m3) annual arithmetic mean concentration. The annual secondary PM2.5 standards are met when the annual arithmetic mean concentration, as determined in accordance with 40 CFR, Part 50, Appendix N, Interpretation of the National Ambient Air Quality Standards for PM2.5, January 15, 2013, is less than or equal to 15.0 ??g/m3. The national annual primary and secondary air quality standards are set forth in 40 CFR Part 50.13, National Primary and Secondary Air Quality Standards for PM2.5, October 17, 2006.







