Title 7 Natural Resources and Environmental Control
1124 Control of Volatile Organic Compound Emissions
41.0 Manufacture of High-Density Polyethylene, Polypropylene and Polystyrene Resins
01/11/1993
41.1 Applicability
41.1.1 The provisions of 41.0 of this regulation applies to the following process Sections at facilities engaged in manufacturing high-density polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene:
41.1.1.1 For manufacturing high-density polyethylene using a liquid-phase slurry process: each material recovery Section and each product finishing Section.
41.1.1.2 For manufacturing polypropylene using a liquid-phase process: each polymerization reaction Section, each material recovery Section, and each product finishing Section.
41.1.1.3 For manufacturing polystyrene using a continuous process: each material recovery Section.
41.1.2 Facilities having all process Sections with uncontrolled emission rates at or below those identified in 41.1.2.1 through 41.1.2.6 of this regulation are exempt from the requirements of 41.0 of this regulation except that owners or operators seeking to comply with 41.0 of this regulation by complying with the uncontrolled emission rates in 41.1.2.1 through 41.1.2.6 of this regulation are still required to comply with the initial certification requirements at 5.0 of this regulation
.
|
Production Process |
Process Section |
Uncontrolled emission rate, megagram of product per year (Mg/yr) | |
41.1.2.1 |
High-density polyethylene, liquid-phase slurry process |
material recovery Section |
7 |
41.1.2.2 |
High-density polyethylene, liquid-phase slurry process |
product finishing Section |
19 |
41.1.2.3 |
Polypropylene, liquid-phase process |
polymerization reaction Section |
7 |
41.1.2.4 |
Polypropylene, liquid-phase process |
material recovery Section |
8 |
41.1.2.5 |
Polypropylene, liquid-phase process |
product finishing Section |
36 |
41.1.2.6 |
Polystyrene, continuous process |
material recovery Section |
7 |
41.1.3 Any facility that becomes or is currently subject to the provisions of 41.0 of this regulation by exceeding the applicability thresholds in 41.1.2 of this regulation will remain subject to these provisions even if its emissions later fall below the thresholds.
41.2 Definitions. As used in 41.0 of this regulation, all terms not defined herein shall have the meaning given them in the November 15, 1990 Clean Air Act Amendments, or in 2.0 of this regulation.
“Continuous process” means a polymerization process in which reactants are introduced continuously and products are removed either continuously or intermittently at regular intervals so that the process can be operated and polymers produced essentially continuously.
“Flame zone” means that portion of the combustion chamber in a boiler occupied by the flame envelope.
“High-density polyethylene” means a linear, thermoplastic polymer comprised of at least 50% ethylene by weight and having a density greater than 0.94 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3) (59 pounds per cubic foot [lb/ft3]).
“Liquid-phase process” means a polymerization process in which the polymerization reaction is carried out in the liquid phase; i.e., the monomer or monomers and any catalyst are dissolved or suspended in a liquid solvent.
“Liquid-phase slurry process” means a liquid-phase polymerization process in which the monomer or monomers are in solution (completely dissolved) in a liquid solvent, but the polymer is in the form of solid particles suspended in the liquid reaction mixture during the polymerization reaction, sometimes called a particle-form process.
“Polypropylene” means a polymer comprised of at least 50% propylene by weight.
“Polystyrene” means a thermoplastic polymer comprised of at least 80% styrene or para-methylstyrene by weight.
“Process line” means a group of equipment assembled that can operate independently if supplied with sufficient raw materials to produce polypropylene, high-density polyethylene, or polystyrene. A process line consists of the equipment in the following process Sections (to the extent that these process Sections are present at a plant): raw materials preparation, polymerization reaction, product finishing, product storage, and material recovery.
“Process Section” means the equipment designed to accomplish a general but well-defined task in polymer production. Process Sections include raw materials preparation, polymerization reaction, material recovery, product finishing, and product storage and may be dedicated to a single process line or common to more than one process line.
“Product finishing Section” means the equipment that treats, shapes, or modifies the polymer or resin to produce the finished end product of the particular facility. Product finishing equipment may extrude and pelletize, cool and dry, blend, introduce additives, cure, or anneal. Product finishing does not include polymerization or shaping such as fiber spinning, molding, or fabricating or modification such as fiber stretching and crimping.
41.3 Standards: High-density polyethylene and polypropylene
41.3.1 The owner or operator of a high-density polyethylene or polypropylene process line containing a process section subject to 41.0 of this regulation shall comply with one of the following:
41.3.1.1 Reduce emissions of total volatile organic compounds (VOCs) by 98 weight %, determined according to the procedure specified in 41.5.1 of this regulation, or to a VOC concentration of 20 parts per million volumetric (ppmv), as determined by the procedure specified in 41.5.2 of this regulation, on a dry basis, whichever is less stringent. Total VOC is expressed as the sum of the actual compounds, not carbon equivalents. If an owner or operator elects to comply with the 20 ppmv concentration standard, the concentration shall include a correction to 3% oxygen only when supplemental combustion air is used to combust the vent stream. The procedure in 41.5.3 of this regulation shall be used to correct the concentration to 3% oxygen.
41.3.1.2 Combust the emissions in a boiler or process heater with a design heat input capacity of 150 million British thermal units per hour (Btu/hr) or greater by introducing the vent stream into the flame zone of the boiler or process heater.
41.3.1.3 Combust the emissions in a flare as follows:
41.3.1.3.1 Flares shall be designed for and operated with no visible emissions as determined by the method specified in 41.5.4.1 of this regulation, except for periods not to exceed a total of five minutes during any two consecutive hours.
41.3.1.3.2 Flares shall be operated with a flame present at all times, as determined by the method specified in 41.5.4.2 of this regulation.
41.3.1.3.3 Flares used to comply with provisions of 41.0 of this regulation shall be steam-assisted, air-assisted, or non-assisted.
41.3.1.3.4 Flares shall be used only with the net heating value of the gas being combusted being 11.2 megajoules per standard cubic meter (MJ/scm) (300 Btu per standard cubic foot [Btu/scf]) or greater if the flare is steam-assisted or air-assisted; or with the net heating value of the gas being combusted being 7.45 MJ/scm (200 Btu/scf) or greater if the flare is nonassisted. The net heating value of the gas being combusted shall be determined by the method specified in 41.5.5.7 of this regulation.
41.3.1.3.5
41.3.1.3.5.1 Steam-assisted and nonassisted flares shall be designed for and operated with an exit velocity, as determined by the method specified in 41.5.5.4 of this regulation, less than 18.3 meters per second (m/s) (60 feet per second [ft/s]), except as provided in 41.3.1.3.5.2 and 41.3.1.3.5.3 of this regulation.
41.3.1.3.5.2 Steam-assisted and nonassisted flares designed for and operated with an exit velocity, as determined by the methods specified in 41.5.5.4 of this regulation equal to or greater than 18.3 m/s (60 ft/s) but less than 122 m/s (400 ft/s) are allowed if the net heating value of the gas being combusted is greater than 37.3 MJ/scm (1,000 Btu/scf).
41.3.1.3.5.3 Steam-assisted and nonassisted flares designed for and operated with an exit velocity, as determined by the methods specified in 41.5.5.4 of this regulation, less than the velocity, V max , as determined by the method specified in 41.5.5.5 of this regulation and less than 122 m/s (400 ft/s) are allowed.
41.3.1.3.6 Air-assisted flares shall be designed and operated with an exit velocity less than the velocity, V max , as determined by the method specified in 41.5.5.6 of this regulation.
41.4 Standards: Polystyrene. The owner or operator of a polystyrene process line containing process Sections subject to 41.0 of this regulation shall comply with one of the following:
41.4.1 Not allow continuous VOC emissions from the material recovery Section to be greater than 0.12 kilogram (kg) VOC per 1,000 kg of product (0.12 lb VOC per 1,000 lb of product).
41.4.2 Not allow the outlet gas stream from each final condenser in the material recovery Section to exceed -25°C (-13°F).
41.5 Test methods and procedures.
41.5.1 The owner or operator shall determine compliance with the percent emission reduction standard in 41.3.1.1 of this regulation as follows:
41.5.1.1 The emission reduction of total VOC shall be determined using the following equation:
![]()
(41-1)
where:
P = Percent emission reduction, by weight.
Einlet = Mass rate of total VOC entering the control device, kg VOC/hr.
Eoutlet = Mass rate of total VOC discharged to the atmosphere, kg VOC/hr.
41.5.1.2 The mass rates of total VOC (Ei, Eo) shall be computed using the following equations:
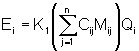
(41-2)
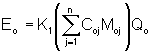
(41-3)
where:
Cij, Coj = Concentration of sample component J of the gas stream at the inlet and outlet of the control device, respectively, dry basis, ppmv.
Mij, Moj = Molecular weight of sample component J of the gas stream at the inlet and outlet of the control device respectively, g/g-mole (lb/lb-mole).
Qi, Qo = Flow rate of the gas stream at the inlet and outlet of the control device, respectively, dscm/hr (dscf/hr).
K1 = 4.157x10-8 [(kg)/(g-mole)]/[(g)(ppm)(dscm)]{5.711x10-15 [(lb)(/(lb-mole)] / [(lb)(ppm)(dscf)]}.
41.5.1.3 Method 18 shall be used to determine the concentration of each individual organic component (Cij, Coj) in the gas stream. Method 1 or 1A, as appropriate, shall be used to determine the inlet and outlet sampling sites. The inlet site shall be before the inlet of the control device and after all product recovery units.
41.5.1.4 Method 2, 2A, 2C, or 2D, as appropriate, shall be used to determine the volumetric flow rates (Qi, Qo). If necessary, Method 4 shall be used to determine the moisture content. Both determinations shall be compatible with the Method 18 determinations.
41.5.1.5 Inlet and outlet samples shall be taken simultaneously. The sampling time for each run shall be one hour in which either an integrated sample or four grab samples shall be taken. If grab sampling is used, then the samples shall be taken at 15-minute intervals.
41.5.2 The owner or operator shall determine compliance with the emission concentration standard in 41.3.1.1 of this regulation as follows:
41.5.2.1 The total VOC concentration is the sum of the individual components and shall be computed for each run using the following equation:
![]()
(41-4)
where:
CVOC = Concentration of total VOC, dry basis, ppmv.
Cj = Concentration of sample component j, ppm.
n = Number of components in the sample.
41.5.2.2 Method 18 shall be used to determine the concentration of each individual inorganic component (Cj) in the gas stream. Method 1 or 1A as appropriate, shall be used to determine the sampling site at the outlet of the control device. Method 4 shall be used to determine the moisture content, if necessary.
41.5.2.3 The sampling time for each run shall be one hour in which either an integrated sample or four grab samples shall be taken. If grab sampling is used, then the samples shall be taken at 15-minute intervals.
41.5.3
41.5.3.1 If supplemental combustion air is used, the total VOC concentration shall be corrected to 3% oxygen and shall be computed using the following equation:
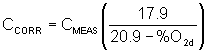
(41-5)
where:
CCORR = Concentration of total VOC corrected to 3% oxygen, dry basis, ppmv.
CMEAS = Concentration of total VOC, dry basis, ppmv, as calculated in 41.5.2.1 of this relation.
%O2d = Concentration of O2, dry basis, percent by volume.
41.5.3.2 The emission rate correction factor, integrated sampling and analysis procedure of Method 3 shall be used to determine the oxygen concentration (%O2d). The sampling site shall be the same as that of the total VOC sample and the samples shall be taken during the same time that the total VOC samples are taken.
41.5.4 When a flare is used to comply with 41.3.1.3 of this regulation:
41.5.4.1 Method 22 shall be used to determine the compliance of flares with the visible emission requirement in 41.3.1.3.1 of this regulation. The observation period is 2 hours and shall be used according to Method 22.
41.5.4.2 The presence of a flare pilot flame shall be monitored using a thermocouple or other equivalent monitoring device to detect the presence of a flame.
41.5.5 The test methods in 40 CFR Part 60, Appendix A (July 1, 1992), shall be used as reference methods for determining the VOC emission rate in terms of kg emission per megagram (Mg) of product, exit velocities, or net heating value of the gas combusted to determine compliance under 41.3 and 41.4 of this regulation as follows:
41.5.5.1 Method 1 or 1A, as appropriate, for selecting the sampling site. The sampling site for the molar composition and vent stream flow rate determination prescribed in 41.5.5.2 and 41.5.5.3 of this regulation shall be prior to the inlet of any combustion device and prior to any dilution of the stream with air.
41.5.5.2 The composition of the process vent stream shall be determined as follows:
41.5.5.2.1 Method 18 and ASTM D2504-67 (reapproved 1977) to measure the concentration of VOC and the concentration of all other compounds present except water vapor and carbon monoxide.
41.5.5.2.2 Method 4 to measure the content of water vapor.
41.5.5.3 The volumetric flow rate shall be determined using Method 2, 2A, 2C, or 2D, as appropriate.
41.5.5.4 The actual exit velocity of a flare shall be determined by dividing the volumetric flow rate (in units of standard temperature and pressure), as determined by Method 2, 2A, 2C, or 2D as appropriate, by the unobstructed (free) cross-Sectional area of the flare tip.
41.5.5.5 The maximum permitted velocity, Vmax, for flares complying with 41.3.1.3.5.1 of this regulation shall be determined using the following equation:
![]()
(41-6)
where:
Vmax = Maximum permitted velocity, m/s.
28.8 = Constant.
31.7 = Constant.
HT = The net heating value as determined in 41.5.5.7 of this regulation.
41.5.5.6 The Vmax for air-assisted flares shall be determined by the following equation:
(41-7)
where:
Vmax = Maximum permitted velocity, m/s.
8.706 = Constant.
0.7084 = Constant.
HT = The net heating value as determined in 41.5.5.7 of this regulation.
41.5.5.7 The net heating value of the process vent stream being combusted in a flare shall be calculated using the following equation:
![]()
(41-8)
where:
HT = Net heating value of the sample, MJ/scm, where the net enthalpy per mole of off-gas is based on combustion at 25°C and 760 millimeters of Mercury (mm Hg) (77°F and 29.92 inches of Mercury [in. Hg]), but the standard temperature for determining the volume corresponding to one mole is 20°C (68°F).
K = Constant:
where standard temperature for
Ci = Concentration of sample components i in ppm on a wet basis, as measured for organics by Method 18 and measured for hydrogen and carbon monoxide by ASTM D1946-82.
Hi = Net heat of combustion of sample component i, kcal/g-mole at 25°C (77°F) and 760 mm Hg (29.92 in. Hg). The heats of combustion of process vent stream components may be determined using ASTM D2382-76 (reapproved 1977) if published values are not available or cannot be calculated.
41.5.5.8 The emission rate of VOC in the process vent stream shall be calculated using the following equation:
![]()
(41-9)
where:
EVOC = Emission rate of total organic compounds in the sample, kilogram per hour (kg/hr).
K = Constant, 2.494x10-6(1/ppm)(g-mole/scm)(kg/g)(min/hr), where standard temperature for (g-mole/scm) is 20°C (68°F).
Ci = Concentration of sample component i, ppm.
Mi = Molecular weight of sample component i, g/g-mole.
Qs = Vent stream flow rate (scm/min), at a standard temperature of 20°C (68°F).
41.5.5.9 The rate of polymer produced, Pp (kg/hr), shall be determined by dividing the weight of polymer pulled in kg from the process line during the performance test by the number of hours (hr) taken to perform the performance test. The polymer pulled, in kg, shall be determined by direct measurement or, subject to prior approval by the Administrator of the U.S. EPA and acceptance as part of a State Implementation Plan (SIP) or Federal Implementation Plan (FIP) revision, computed from materials balance by good engineering practice.
41.5.5.10 The emission rate of VOC in terms of kilograms of emissions per megagram of production shall be calculated using the following equation:
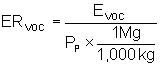
(41-10)
where:
ERVOC = Emission rate of VOC, kg VOC/Mg product.
EVOC = Emission rate of VOC in the sample, kg/hr.
PP = The rate of polymer produced, kg/hr.
41.6 Recordkeeping. The owner or operator of a facility subject to 41.0 of this regulation shall maintain the following records in a readily accessible location for at least five years and shall make these records available to the Department upon verbal or written request:
41.6.1 For facilities complying with the standards listed in 41.3.1.1 of this regulation, parameters listed in 41.5.1, 41.5.2, and, where applicable, 41.5.5 of this regulation.
41.6.2 For facilities complying with the standards listed in 41.3.1.2 of this regulation, parameters listed in 41.5.3, and, where applicable, 41.5.5 of this regulation.
41.6.3 For facilities complying with the standards listed in 41.3.1.3 of this regulation, parameters listed in 41.5.4, and, where applicable, 41.5.5 of this regulation.
41.6.4 For facilities complying with the standards listed in 41.4 of this regulation, parameters listed in 41.5.5 of this regulation where applicable.
41.6.5 For all facilities containing sources subject to 41.0 of this regulation, the following records shall be kept:
41.6.5.1 The time, date, and duration of any excess emissions.
41.6.5.2 The subject source of any excess emissions.
41.6.5.3 The cause of any excess emissions.
41.6.5.4 The estimated rate of emissions (expressed in the units of the applicable emission limitation) and the operating data and calculations used in determining the magnitude of any excess emissions.
41.6.5.5 Any corrective actions and schedules utilized to correct the conditions causing any excess emissions.
41.7 Reporting requirements. The owner or operator of any facility containing sources subject to 41.0 of this regulation shall:
41.7.1 Comply with the initial compliance certification requirements of 5.1 of this regulation.
41.7.2 Comply with the requirements of 5.2 of this regulation for excess emissions related to the control devices required to comply with 41.3.1.2, 41.3.1.3, or 41.4.2 of this regulation, as well as any other State of Delaware exceedance reporting requirements.


