department of natural resources and environmental control
Division of Air and Waste Management
final
Secretary’s Order No. 2009-A-0028
Date of Issuance: August 14, 2009
Effective Date: September 10, 2009
Under the authority vested in the Secretary of the Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control (Department), the following findings, reasons and conclusions are entered as an Order of the Secretary in the above-referenced matter.
Procedural History
On February 22, 2009, the Department’s issued Start Action Notice #2009-03, which approved Division of Air and Waste Management, Air Quality Management Section’s (AQMS) request to begin the formal regulatory development process to amend 7 DE Admin. Code 1101, Definitions and Administrative Principles. AQMS prepared a proposed regulation to revise Section 2.0’s definition of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). The Department had the proposed regulation published in the May 1, 2009 Delaware Register of Regulations and notice was published in newspapers of general circulation. The public notices also included a scheduled May 26, 2009 public hearing to be held in AQMS’ office in Dover.
The Department received three comments in support of the proposed regulation within the public comment period that began May 1, 2009 and ended thirty day later, as required by Delaware’s Administrative Procedures Act, 29 Del.C. §10118(a). The Department held a public hearing before presiding Hearing Officer Robert P. Haynes. Department representatives, Gene Pettingill and Ron Amirikian, of AQMS attended the public hearing, but no member of the public attended. The Department’s expert responsible for drafting the proposed regulation, Gene Pettingill, developed the administrative record to support the proposed regulation and the exhibits and the transcript of the hearing constitute the entire record as recommended by the presiding hearing officer. Mr. Haynes, based upon no public comments in opposition and the public hearing record, recommended no need to further develop the record, and he prepared a draft order and accompanying Report dated August 13, 2009 that recommends adoption of the proposed regulation as a final regulation without any change.
Findings
This Order considers a draft revision prepared by AQMS to reflect certain changes made by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to the definition of VOCs. I find that the proposed regulation reflects EPA’s determination that certain VOCs have neglible photochemical reactivity and has exempted them from federal regulation as ground-level ozone precursors. I find that this will impact Delaware users of certain products such as coatings, adhesives, cleaning compounds, aerosol propellants, and blowing agents from regulation as sources of air emissions of VOCs. Based upon the record developed, I find that the proposed regulation is reasonable and supported by maintaining consistency between the federal and state regulation of VOCs as defined by EPA in the Department’s Regulations. The Regulations follow the regulatory scheme established by EPA. The federal definition of VOCs
changed and the proposed revision tracks the federal change so that Delaware’s regulation of VOCs emissions will regulate the same substances as the federal regulation. Consequently, this Order approves the proposed regulation as a final regulation based upon the record and the information developed at the public hearing.
In conclusion, the following findings and conclusions are entered:
1. The Department, acting through this Order of the Secretary, hereby approves as reasonable the proposed regulation and the record in support of the proposed regulation, and adopts as a final regulation the proposed regulation published in the May 1, 2009 Delaware Register of Regulations and attached hereto as Appendix A; and
2. The Department shall have this Order published in the Delaware Register of Regulations and in newspapers in the same manner as the notice of the proposed regulation.
David S. Small, Acting Secretary
1101 Definitions and Administrative Principles
The words and phrases defined and the administrative principles presented in this regulation shall apply to all regulations, unless the context clearly indicates otherwise.
09/11/1999 xx/xx/2009
“Accumulator” means the reservoir of a condensing unit receiving the condensate from the condenser.
“Act” means 7 Del.C., Ch 60, approved July 17, 1973, as amended July 26, 1974.
“Active section of disposal site” means any disposal site other than an inactive section.
“Activity” means construction, or operation, or use of any facility, property, or device.
“Actual operating conditions” means any conditions or operating parameters, or the quantities representing these conditions or parameters, which exist during any operation.
“Adequately wetted” means sufficiently mixed or coated with water or an aqueous solution to prevent dust emissions.
“Air contaminant” means particulate matter, dust, fumes, gas, mist, smoke, or vapor of any combination thereof, exclusive of uncombined water.
“Air contaminant control device or system” means any method, process, equipment, or stack which removes, reduces, or renders less noxious air contaminants discharged into the atmosphere.
“Air contaminant source” means any source from which there is emitted into the atmosphere any air contaminant regardless of who owns the property or facility from which the emission comes. Without limiting the generality of the foregoing, this term includes all types of commercial and industrial plants and works, heating and power plants and stations, shops and stores; buildings and other structures of all types, including single and multiple family residences, apartment houses, office buildings, public buildings, hotels, restaurants, schools, hospitals, churches, and other institutional buildings, automobiles, trucks, tractors, busses and other motor vehicles (hereinafter called "motor vehicles"); garages, vending and service locations and stations; railroad locomotives; ships, boats and other waterborne craft; airborne crafts; portable fuel‑burning equipment; incinerators of all types, indoor and outdoor; and refuse dumps and piles.
“Air pollution” means the presence in the outdoor atmosphere of one or more air contaminants in sufficient quantities and of such characteristics and duration as to be injurious to human, plant, or animal life or to property or which unreasonably interferes with the enjoyment of life and property within the jurisdiction of the State, excluding all aspects of employer‑employee relationships as to health and safety hazards.
“Air quality criteria” means a series of observed relationships between air pollutants and their effects on health, welfare, vegetation, or property. Criteria for any given effect are expressed in terms of pollutant concentrations, duration of exposure and method of measurement.
“Air quality standard” means an air quality level as established by Regulations in terms of a limit on contaminant levels in the atmosphere. Such standards shall be consistent with the air quality criteria.
“Air stagnation” means a weather situation characterized by limited horizontal and vertical mixing.
“Air stagnation advisory” means the National Weather Service method of advising of the existence of air stagnation over a discrete area.
“Allowable emissions”: See 1.9 of 7 DE Admin. Code 1125.
“Alteration”: See "Modification".
“Alternative method” means any method of sampling and analyzing for an air pollutant which is not a reference method or an equivalent method but which has been demonstrated to the Secretary's satisfaction to produce in specific cases, results adequate for his determination of compliance.
“Ambient air” means atmosphere.
“Asbestos” means Actimolite, Amosite, Anthophyllite, Chrysotile, Crocidolite, Tremolite.
“Asbestos containing waste material” means any waste which contains commercial asbestos and is generated by a source subject to the provisions of 7 DE Admin. Code 1121, including asbestos mill tailings, control device asbestos waste, friable asbestos waste material, and bags or containers that previously contained commercial asbestos.
“Asbestos material” means asbestos or any material containing asbestos.
“Asbestos mill” means any facility engaged in the conversion or any intermediate step in the conversion of asbestos ore into commercial asbestos. Outside storage of asbestos material is not considered a part of such facility.
“Asbestos tailings” means any solid waste product of asbestos mining or milling operations which contain asbestos.
“Asphalt” means a dark brown to black cementitious material (solid, semisolid, or liquid in consistency) in which predominating constitutents are bitumens which occur in nature as such or which are obtained as residue in refining petroleum.
“Asphalt concrete plant” means any combination of the following: dryers, systems for screening, handling, storing, and weighing hot aggregate; systems for loading, transferring, and storing mineral filler; systems for mixing asphalt concrete; and the loading transfer, and storage systems associated with emission control systems.
“Atmosphere” means the air that envelops or surrounds the earth and includes all spaces outside of buildings, stack or exterior ducts.
“Automobile” means all passenger cars or passenger car derivatives capable of seating 12 or fewer passengers.
“Auxiliary burner” means equipment to supply additional heat, by the combustion of auxiliary fuel, for the purpose of obtaining temperatures sufficiently high (a) to dry and ignite waste material, (b) to maintain ignition thereof, and (c) to promote complete combustion of combustible solids, liquids, and gasses.
“Auxiliary heat input” means the heat value of an auxiliary fuel provided to promote complete combustion.
“Background concentration” means the concentration of an air contaminant which is due to natural sources.
“Beryllium” means the element beryllium. Where weight or concentrations are specified, such weights or concentrations apply to beryllium only, excluding the weight or concentration of any associated elements.
“Beryllium alloy” means any metal to which beryllium has been added in order to increase its beryllium content and which contains more than 0.1% beryllium by weight.
“Beryllium containing waste” means material contaminated with beryllium or beryllium compounds used or generated during any process or operation performed by a source.
“Beryllium ore” means any naturally occurring material mined or gathered for its beryllium content.
“Best available control technology”: See 1.9 of 7 DE Admin Code 1125.
“Boiler lancing” means the operation of removing soot, slag, or fly ash from the walls of the firebox, generating tubes, and other parts of fuel burning equipment.
“Bottom filling” means the filling of a tank truck or stationary storage tank through an opening that is flush with the tank bottom.
“British thermal unit” means the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water one degree Fahrenheit at or near its point of maximum density (39.1oF), usually abbreviated as BTU.
“Bulk gasoline plant” means a gasoline storage and distribution facility with an average daily throughput equal to or less than 76,000 liters (20,000 gallons) which receives gasoline from bulk terminals by trailer transport, stores it in tanks, and subsequently dispenses it via account trucks to local farms, businesses, and service stations.
“Bulk gasoline terminal” means a gasoline storage facility which receives gasoline from its supply source primarily by pipeline, ship, or barge, and delivers gasoline to bulk gasoline plants or to commercial or retail accounts primarily by tank truck; and has an average daily throughput of more than 76,000 liters (20,000 gallons) of gasoline.
“Capital expenditure” means an expenditure for a physical or operational change to an existing facility which exceeds the product of the applicable "annual assets guideline repair allowance percentage" specified in the latest edition of Internal Revenue Service Publication 534 and the existing facility basis, as defined by Section 1012 of the Internal Revenue Code. However, the total expenditure for a physical or operational change to an existing facility must not be reduced by any "excluded additions" as defined in Internal Revenue Service Publication 534, as would be done for tax purposes.
“Capacity factor” means the ratio of the average load on a machine or equipment for the period of time considered to be the capacity rating of the machine.
“Cell room” means a structure or structures housing one or more mercury electrolytic chlor‑alkali cells.
“Ceramic plant” means a manufacturing plant producing ceramic items.
“Ceremonial fires” mean bonfires used for ceremonies sponsored by educational, cultural, or religious institutions.
“Clear coat” means a coating which lacks color and opacity or is transparent and uses the undercoat as a reflectant base or undertone color.
“Coal refuse” means waste‑product of coal mining, cleaning, and coal preparation operation (e.g. culm, gob, etc.) containing coal, matrix material, clay, and other organic and inorganic material.
“Coating line” means one or more apparatus or operations which include a coating applicator, flash‑off area, and oven wherein a surface coating is applied, dried, or cured.
“Coating or printing”: Coating is the application of a uniform layer of material across the entire width of a web. Printing is the formation of words, designs, and pictures, usually by a series of application rolls each with only partial coverage.
“Coil coating” means the coating of any flat metal sheet or strips that comes in rolls or coils.
“Cold cleaning” means the batch process of cleaning and removing soils from metal surfaces by spraying, brushing, flushing or immersion while maintaining the solvent below its boiling point. Wipe cleaning is not included in this definition.
“Combustion contaminant” means any air contaminant discharged into the atmosphere by reason of a combustion operation.
“Combustion operation” means any operation which causes or results in the burning of any type of material.
“Comfort heating equipment” means fuel burning equipment designed to heat the interior of a building or dwelling for the sole purpose of providing comfort for the inhabitants of the structure.
“Comfort ventilation equipment” means equipment producing an emission into the open air resulting from the cooling of the interior of a building or dwelling for the sole purpose of providing comfort for the inhabitants of the structure.
“Commence” means to undertake a continuous program of construction or modification or to enter into a contractual obligation to undertake and complete, within a reasonable time, a continuous program of construction or modification.
“Commercial asbestos” means any variety of asbestos which is produced by extracting asbestos from asbestos ore.
“Compliance schedule” means the date or dates by which a source or category of sources is required to comply with standards of these regulations and with any steps toward such compliance.
“Component” means any piece of equipment which has the potential to leak volatile organic compounds when tested in the manner described in 14.4 of 7 DE Admin. Code 1124. These sources include, but are not limited to pumping seals, compressor seals, seal oil degassing vents, pipeline valves, flanges and other connections, pressure relief devices, process drains and open ended pipes. Excluded from these sources are valves which are not externally regulated.
“Condensate” means hydrocarbon liquid separated from natural gas which condenses due to changes in the temperature or pressure and remains liquid at standard conditions.
“Condenser” means any heat transfer device used to liquefy vapors by removing their latent heats of vaporization. Such devices include, but are not limited to, shell and tube, coil, surface, or contact condensers.
“Condenser stack gases”: As it applies to 7 DE Admin. Code 1121, condenser stack gases means the gaseous effluent evolved from the stack of processes utilizing heat to extract mercury metal from mercury ore.
“Conservation practices” means land treatment techniques designed to conserve, enhance, or protect soil, water, vegetation, and other natural resources.
“Construction” means fabrication, erection, or installation of an applicable source or a stationary source.
“Construction, installation, alternation or modification permit” means written notice that the construction, installation or alteration of an air contaminant source or control device has been approved by the Department.
“Container” means any portable enclosure in which a material is stored, managed or transported.
“Contamination” means the degradation of naturally occurring water, air, or soil quality either directly or indirectly as a result of the transfer of diseased organisms, blood or other matter that may contain disease organisms from one material or object to another.
“Continuous monitoring system” means the total equipment, required under the emission monitoring section in applicable subsections used to sample and condition (if applicable), to analyze, and to provide a permanent record of emissions or process parameters.
“Control device asbestos waste” means any asbestos‑containing waste material that is collected in a control device.
“Conveyorized degreaser” means any continuous system which transports metallic objects through a bath containing organic solvent for the purpose of cleaning or degreasing.
“Crude oil” means a naturally occurring mixture which consists of hydrocarbons or sulfur, nitrogen or oxygen derivatives of hydrocarbons and which is a liquid at standard conditions.
“Custody transfer” means the transfer of produced petroleum or condensate, after processing and/or treating in the producing operations, from storage tanks or automatic transfer facilities to pipelines or any other forms of transportation.
“Cutback asphalt” means asphalt cement which has been liquefied by blending with petroleum solvents. (diluents). Upon exposure to atmospheric conditions the diluents evaporate, leaving the asphalt cement to perform its function.
“Day” means 24 consecutive hours.
“Delivery vessel” means tank trucks or trailers equipped with a storage tank and used for the transport of gasoline from sources of supply to stationary storage tanks.
“Demolition”: As it applies to 7 DE Admin. Code 1121, demolition means the wrecking or taking out of any load‑supporting structural member and any related removing or stripping of friable asbestos materials.
“Denuder” means a horizontal or vertical container which is part of a mercury chlor‑ alkali cell and in which water and alkali metal amalgam are converted to alkali metal hydroxide, mercury, and hydrogen gas in a short‑circuited, electrolytic reaction.
“Department” means the Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control as defined in 29 Del.C., Ch 80, as amended.
“Desulfurized fuel gas” means a fuel gas with the sulfur content reduced to less than 10 grains of H2S per one hundred (100) standard cubic feet of fuel gas.
“Difficult-to-monitor valves” means any valve which cannot be monitored without elevating the monitoring personnel more than 2 meters above a support surface.
“Distillate fuel oil” means any liquid fuel derived directly or indirectly as the distilled product of crude petroleum, and having a maximum Saybolt Universal viscosity of 40 seconds at 100oF.
“Division” means the Division of Air and Waste Management.
“Drilling and production facility” means all drilling and servicing equipment wells flow lines separators, equipment, gathering lines and auxiliary non‑ transportation‑related equipment used in the production of petroleum but does not include natural gasoline plants.
“Dry cleaning facility” means a facility engaged in the cleaning of fabrics in an essentially non-aqueous solvent by means of one or more washes in solvent, extraction of excess solvent by spinning, and drying by tumbling in an air stream. The facility includes but is not limited to any washer, dryer or filter and purification systems, waste disposal systems, holding tanks, pumps and attendant piping and valves.
“Effective stack height” means the sum of the stack height and the rise of the stack gases above the stack due to the exit velocity and the temperature of the gases.
“Emergency renovation”: As it applies to 7 DE Admin. Code 1121, emergency renovation means a renovation operation that results from a sudden, unexpected event, and is not a planned renovation. Operations necessitated by non‑ routine failure of equipment are included.
“Emission” means the release or discharge, whether directly or indirectly, of any air pollutant into the ambient air from any source.
“Emission standard” means a regulation (or portion thereof) setting forth an allowable rate of emissions, level of opacity, or prescribing equipment or fuel specifications that result in control of air contaminant emissions.
“Emulsified asphalt” means an emulsion of asphalt cement and water which contains a small amount of an emulsifying agent.
“End box” means a container or containers located on one or both ends of a mercury chlor‑alkali electrolyzer which serves as a connection between the electrolyzer and denuder for rich and stripped amalgam.
“End box ventilation system” means a ventilation system which collects mercury emissions from the end boxes, the mercury pump sumps, and their water collection systems.
“Engineering guide” means a statement of guidelines, engineering factors to be considered, standards established, or general procedures to be followed in meeting the requirements of various regulations adopted by the Department.
“Equipment shutdown” means the process of taking a unit of equipment off‑line from an operative condition to an inoperative condition. (Applicable to 7 DE Admin. Code 1120 and 1121).
“Equipment shutdown” means the process of taking a unit of equipment off‑line from an operative condition such that normal production rates are not being achieved.
“Equipment start-up” means the process of bringing a unit of equipment on‑line from an inoperative condition such that normal production rates are being achieved.
“Equivalent method” means any method of sampling and analyzing for an air pollutant which has been demonstrated to the Secretary's satisfaction to have a consistent and quantitatively known relationship to the referenced method under specified conditions.
“Etiologic agents” mean organisms defined to be etiologic agents (causative agent of a disease or diseases) in Title 49 of the U.S. Code of Federal Regulations at 173.386 (October 1, 1987 Edition).
“Excess emissions” means emissions of an air contaminant in excess of an emission standard.
“Existing installation,equipment, source or operation” means any air contaminant source the construction or modification of which was commenced before the date of adoption of any applicable regulation or standard. As this definition applies to 7 DE Admin. Code 1120, New Source Performance Standards, it means any air contaminant source the construction or modification of which was commenced before August 17, 1971. As this definition applies to 7 DE Admin. Code 1121. Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants, it means any air contaminant source the construction or modification of which was commenced before March 31, 1971.
“Extraction plant”: As it applies to 7 DE Admin. Code 1121, extraction plant means a facility chemically processing beryllium ore to beryllium metal, alloy, or oxide, or performing any of the intermediate steps in these processes.
“Fabricating”: As it applies to 7 DE Admin. Code 1121, fabricating means any processing of a manufactured product containing commercial asbestos, with the exception of processing at temporary sites for the construction or restoration of buildings, structures, facilities, or installations.
“Fabric coating” means the coating of a textile substrate with a knife, roll or rotogravure coater to impart properties that are not initially present, such as strength, stability, water or acid repellency, or appearance.
“Final repair coating” means the final surface coatings applied to correct topcoat imperfections.
“Firebox” means the chamber or compartment of a boiler or furnace in which materials are burned but does not mean the combustion chamber of an incinerator.
“Flare” means an engineered device designed to burn waste gases from process operation or relief valves.
“Floating roof” means a storage vessel cover consisting of a double deck, pontoon single deck, internal floating cover or covered floating roof, which rests upon and is supported by the petroleum liquid being contained, and is equipped with a closure seal or seals to close the space between the roof edge and tank wall.
“Flue”: See “Stack”.
“Flue gas” means products of combustion which are transported through a flue.
“Fly ash” means any particles of gas‑borne solid matter resulting from the combustion of any solid fuel but excluding process emissions.
“Forebays” means the primary sections of a wastewater separator.
“Fossil fuel” means natural gas, petroleum, coal and any form of solid, liquid, or gaseous fuel derived from such materials for the purpose of creating useful heat.
“Foundry”: As it applies to 7 DE Admin. Code 1121, foundry means a facility engaged in the melting or casting of beryllium metal or alloy.
“Freeboard height” means for a vapor degreaser, the distance from the solvent vapor level in the tank to the lip of the degreaser tank. For a cold cleaner, the distance from the liquid solvent level in the degreaser tank to the lip of the tank.
“Freeboard ratio” means the freeboard height divided by the width of the degreaser.
“Friable asbestos material” means any material that contains more than 1% asbestos by weight and that can be crumbled, pulverized, or reduced to powder, when dry, by hand pressure.
“Fuel” means any combustible matter including, but not limited to coal, gas, oil, and refuse.
“Fuel burning equipment” means each unit, or any combination of units discharging to a common stack used for the burning of fuel or other combustible material for the primary purpose of utilizing the thermal energy released.
“Garbage” means animal or vegetable waste matter originating in houses, kitchens, restaurants, hotels, produce markets or similar installations.
“Gas service” means equipment which processes, transfers or contains one or more volatile organic compounds in the gaseous phase.
“Gasoline” means any petroleum distillate having a Reid vapor pressure of 27.6 kPa (4 pounds per square inch) or greater and used as automotive fuel.
“Gasoline dispensing facility” means any site where gasoline is dispensed to motor vehicle gasoline tanks from stationary storage vessels.
“Good engineering practice stack height”: See 7 DE Admin. Code 1127.
“Hazardous particulate matter” means particulate matter which poses special health hazards due to chemical or biological reactivity or particle size.
“Heat input” means the potential thermal energy resulting from the complete combustion of any fuel.
“Hot well” means the reservoir of a condensing unit receiving the warm condensate from the condenser.
“Hourly period”: See “One hour period”.
“Hydrocarbon” means any organic compound consisting predominantly of carbon and hydrogen.
“Hydrogen gas steam”: As it applies to 7 DE Admin. Code 1121, hydrogen gas stream means a hydrogen stream formed in the chlor‑alkali cell denuder.
“Inactive section of disposal site” means any disposal site or portion thereof where additional asbestos waste material will not be deposited and where the surface is not disturbed by vehicular traffic.
“Incineration” means the process of igniting and burning solid, semi‑solid, liquid, or gaseous combustible waste to their products of combustion.
“Incinerator” means any enclosure device used to destroy waste material by using controlled flame combustion.
“Indirect heat exchange” means transfer of thermal energy in such a manner that the material being heated is not contacted by and adds no substance to the products of combustion.
“Industrial waste” means any waste produced by a manufacturing process.
“Infectious waste” means those solid wastes which may cause human disease and may reasonably be suspected of harboring human pathogenic organisms, or may pose a substantial present or potential hazard to human health or the environment when improperly treated, stored, transported, disposed of or otherwise managed. Types of solid wastes designated as infectious include but are not necessarily limited to the following:
Biological wastes:
a. Biological liquid wastes means blood and blood products, excretions, exudates, secretions, suctionings and other body fluids including liquid wastes from renal dialysis.
b. Pathological wastes means all human tissues and anatomical remains, including human fetal remains which emanate from surgery, obstetrical procedures, autopsy and laboratory procedures.
c. Cultures and stocks of etiologic agents and associated biologicals wastes means, but is not limited to, specimen cultures, cultures and stocks of etiologic agents, and wastes from production of biologicals and serums.
d. Laboratory wastes means those wastes which have come in contact with pathogenic organisms or blood or body fluids. Such wastes include, but are not limited to, disposable materials; culture dishes; devices used to transfer, inoculate and mix cultures; paper and cloth which has come in contact with specimens or cultures which have not been sterilized or rendered noninfectious; or laboratory wastes, including cultures of etiologic agents, which pose a substantial threat to health due to their volume and virulence.
e. Animal tissue, bedding and other waste from animals known or suspected to be infected with a pathogen which also causes human disease, provided that prevailing evidence indicates that such tissue, bedding or other waste may act as a vehicle of transmission to humans.
f. Human dialysis waste materials including blood lines and dialysate membranes.
Sharps means any discarded article that may cause puncture or cuts. Such wastes include but are not limited to, needles, intravenous (IV) tubing with needles attached, scalpel blades, glassware, and syringes that have been removed from their original sterile containers.
Discarded Biologicals means serums and vaccines produced by pharmaceutical companies for human or veterinary use. These products may be discarded because of a bad manufacturing lot (i.e., off‑specification material that does not pass quality control or that is recalled), out‑dating or removal of the product from the market or other reasons. Because of the possible presence of etiologic agents in these products, the discarded material constitutes infectious waste.
Other infectious wastes means any residue or contaminated soil, water, or other debris resulting from the cleanup of a spill of any infectious waste.
“Isokinetic sampling” means sampling in which the linear velocity of the gas entering the sampling nozzle is equal to that of the undisturbed gas stream at the sample point.
“Large appliances” means doors, cases, lids, panels and interior support parts of residential and commercial washers, dryers, ranges, refrigerators, freezers, water heaters, dishwashers, trash compactors, air conditioners and other similar products.
“Large incinerator” means an incinerator which has a capacity of greater than 1000 pounds per hour.
“Light duty truck” means any motor vehicle rated at 3864 kilograms (8500 pounds) gross weight or less which is designed primarily for the purpose of transportation or are derivatives of such vehicles.
“Linear extrapolation” means a technique for determining an unknown value lying numerically outside the range of a series of values which is in direct linear proportion to another series of known values by comparing the two series, utilizing the following equation;
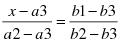
where:
x = The unknown value;
a2 = Any known value in the series containing the unknown value;
a3 = Any known value, other than a2, in the series containing the unknown value;
b1 = The value in the series of known values corresponding to x;
b2 = The value in the series of known values corresponding to a2;
b3 = The value in the series of known values corresponding to a3.
“Linear interpolation” means a technique for determining an unknown value lying numerically inside the range of a series of values which is in direct linear proportion to another series of known values by comparing the two series, utilizing the equation set forth under the definition of Linear Extrapolation of this Regulation.
“Liquid service” means equipment which processes, transfers or contains one or more volatile organic compounds as a liquid having a Reid vapor pressure greater than 0.1 psia.
“Lowest achievable emission rate (LAER)” means the rate of emissions based on the following, whichever is more stringent.
The most stringent emission limitation which is contained in the implementation plan of any State for such class or category of source, unless the owner or operator of the proposed source demonstrates that such limitations are not achievable; or
The most stringent emission limitation which is achieved in practice by such class or category of source.
This term, applied to a modification, means the lowest achievable emission rate for the new or modified facilities within the source. In no event shall the application of this term permit a proposed new or modified facility to emit any pollutant in excess of the amount allowable under new source standards of performance.
“Machine shop” means a facility performing cutting, grinding, turning, honing, milling, deburring, lapping, electrochemical machining, etching, or other similar operations.
“Malfunction” means any sudden and unavoidable failure of air pollution control equipment or of a process to operate in a normal or usual manner. Failures that are caused entirely or in part by poor maintenance, careless operation, or any other preventable upset condition or preventable equipment breakdown shall not be considered malfunctions.
“Manufacturing”: As it applies to 7 DE Admin. Code 1121, manufacturing means the combining of commercial asbestos, or in the case of woven friction products the combining of textiles containing commercial asbestos, with any other material or materials including commercial asbestos, and the processing of this combination into a product.
“Manufacturing process” means any process principally operated for the purpose of producing any durable or consumable good or goods.
“Mass emission rate” means the weight of any air contaminant discharged per unit of time.
“Material” means any gas, liquid, or solid or any combination thereof.
“Mercury” means the element mercury, excluding any associated elements, and includes mercury in particulates, vapors, aerosols, and compounds.
“Mercury chlor-alkali cell” means a device which is basically composed of an electrolyzer section and a denuder (decomposer) section and utilizes mercury to produce chlorine gas, hydrogen gas, and alkali metal hydrozide.
“Mercury chlor-alkali electrolyzer” means an electrolytic device which is part of a mercury chlor‑alkali cell and utilizes a flowing mercury cathode to produce chlorine gas and alkali metal amalgam.
“Mercury ore” means a mineral mined specifically for its mercury content.
“Mercury ore processing facility” means a facility processing mercury ore to obtain mercury.
“Metal furniture coating” means the surface coating of any furniture made of metal or any metal part which will be assembled with other metal, wood, fabric, plastic or glass parts to form a furniture piece.
“Metropolitan Philadelphia Interstate Air Quality Control Region” means a geographical region composed of Burlington, Camden, Gloucester, Mercer, and Salem Counties in the State of New Jersey; Bucks, Chester, Delaware, Montgomery, and Philadelphia Counties in the State of Pennsylvania; and New Castle County in the State of Delaware.
“Modification” means any physical change in, or change in the method of operation of, any air contaminant source which results in an emission to the atmosphere of a new air contaminant or an increase in the emission rate to the atmosphere of one or more existing air contaminants. Upon modification, an existing source shall become subject to 7 DE Admin. Code 1120 only with respect to those pollutants which, after modification, are either newly emitted, or emitted at an increased rate. Routine maintenance, repair and replacement shall not be considered a modification. Conversion to coal required for energy considerations, as specified in Section 113 (d) (5) of the 1977 Clean Air Act, shall not be considered a modification. The relocation of an existing facility shall be considered a modification whenever the Department determines it necessary to maintain ambient air quality standards. Change in ownership of an existing facility shall not be considered a modification. This definition shall not apply to 7 DE Admin. Code 1125.
“Monitoring device” means the total equipment, required under the monitoring of operations sections in applicable sub‑sections used to measure and record (if applicable) process parameters.
“National Ambient Air Quality Standards” means those primary and secondary ambient air quality standards which are promulgated by the Administrator of the Federal Environmental Protection Agency.
“National Weather Service” means an agency of the United States Commerce Department charged with the responsibility of providing weather information and service to the public and to commercial aviation.
“Natural source” means any air contaminant source which is not man‑made.
“New installation, equipment, source, operation” means any air contaminant source the construction or modification of which is commenced after the date of adoption of any applicable regulation or standard. As this definition applies to 7 DE Admin. Code 1120, New Source Performance Standards, it means any air contaminant source the construction or modification of which was commenced after August 17, 1971. As this definition applies to 7 DE Admin. Code 1121, Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants, it means any air contaminant source the construction or modification of which was commenced after March 31, 1971. This definition shall not apply to 7 DE Admin. Code 1125.
“Nitric acid production unit” means any facility producing weak nitric acid by either the pressure or atmospheric pressure process.
“Nitrogen oxides” means all oxides of nitrogen measured by test methods set forth herein. (Applicable to 7 DE Admin. Code 1120).
“Nitrogen oxides” means nitric oxide (NO) or nitrogen dioxide (NO2) or any combination thereof.
“Noninfectious” means a state in which potentially harmful microorganisms are absent, free of pathogens.
“Odor” means that property of an air contaminant that affects the sense of smell.
“One hour period” means any consecutive 60 minute period.
“Opacity” means that condition which renders material partially or wholly impervious to rays of light and causes a degree of obstruction to an observer's view.
“Open air”: See “Atmosphere”.
“Open burning” means any outdoor fire or outdoor smoke producing process from which the products of combustion are emitted directly into the ambient air. This does not include incinerators, boilers, or heaters used in process operations.
“Open top vapor degreaser” means the batch process of cleaning and removing soils from metal surfaces by condensing hot solvent vapor on the colder metal parts.
“Operating permit” means written notice that the operation of any air contaminant source or control device has been approved by the Department.
“Outside air”: See “Atmosphere”
“Owner or operator”: See “Person”
“Packaging rotogravure printing” means rotogravure printing upon paper, paper board, metal foil, plastic film or other substrates, which are subsequently formed into containers and labels for articles to be sold.
“Paint application transfer efficiency” means the percentage of coating solids which leave the coating applicator and remain on the surface of the product.
“Paper coating” means coatings applied to paper and pressure‑sensitive tapes regardless of substrata. Related webcoating processes on plastic films and decorative coatings on metal foil are included in this definition.
“Particulate asbestos material” means finely divided particles of asbestos material.
“Particulate matter” means material, other than uncombined water, which is suspended in or discharged into the atmosphere as a liquid or solid.
“Penetrating prime coat” means an application of low viscosity liquid asphalt to an absorbent surface. It is used to prepare an untreated base for an asphalt surface. The prime penetrates the base and plugs the voids, hardens the top, and helps bind it to the overlying asphalt course. It also reduces the necessity of maintaining an untreated base course prior to placing the asphalt pavement.
“Person” meansany individual, firm, association, organization, partnership, business trust, corporation, company, contractor, supplier, installer, developer, user or owner or operator, or any Federal, State or Local governmental agency or public district or any officer or employee thereof.
“Petroleum” means the crude oil removed from the earth and the oils derived from tar sands, shale, and coal.
“Petroleum liquids” means petroleum, condensate, and any finished or intermediate products manufactured in a petroleum refinery but does not mean Number 2 through Number 6 fuel oils as specified in ASTM‑D‑396‑69, gas turbine fuel oils Numbers 2‑GT through 4‑GT as specified in ASTM‑D‑2880‑71, or diesel fuel oils Numbers 2‑D and 4‑D as specified in ASTM‑D‑975‑68.
“Petroleum refinery” means any facility engaged in producing gasoline, aromatics, kerosene, distillate fuel oils, residual fuel oils, lubricants, asphalt or other products through distillation of petroleum or through redistillation, cracking rearrangement or reforming of unfinished petroleum derivations.
“Planned renovation”: As it applies to 7 DE Admin. Code 1121, planned renovation means a renovation operation, or a number of such operations, in which the amount of friable asbestos material that will be removed or stripped within a given period of time can be predicted. Operations that are individually non‑scheduled are included, provided a number of such operations can be predicted to occur during a given period of time based on operating experience.
“PM2.5” means particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter of less than or equal to a nominal 2.5 micrometers, as determined by the appropriate reference methods.
“PM10” means particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter less than or equal to a nominal 10 micrometers, as determined by appropriate reference methods.
“Potential to emit”: See 1.9 of 7 DE Admin. Code 1125.
“Pothole” means a hole or pit in a road surface generally caused by successive freezing and thawing temperature of the road surface aggravated by vehicular traffic.
“Prescribed burning” means open burning under such conditions that the fire is confined to a predetermined area.
“Prilling operation” means any solidification process which employs the mechanism of molten droplets in free fall through a heat exchange medium.
“Primary ambient air quality standards” means those ambient air quality standards which, in the judgment of the Department, are requisite to protect the public health and allow an adequate margin of safety.
“Prime coat” means the first film of coating applied in a surface‑coating operation.
“Printing or coating”: See “Coating and Printing”.
“Private dwelling” means a domestic residence housing no more than three families and where no commercial or industrial activity is carried on.
“Process emission” means discharge into the atmosphere of air contaminants resulting from a specific process or combination of processes.
“Process operation” means any chemical, industrial, or manufacturing operation including, but not limited to, heat transfer, fluid flow, evaporation, humidification, absorption, extraction, distillation, drying, mixing, classification, sedimentation, decantation, filtration, crystallization, centrifugation, disintegration and material handling.
“Process weight rate”: A rate established as follows:
(a) For continuous or long‑run steady‑state source operations, the total process weight for the entire period of continuous operation or for a typical portion thereof, divided by the number of hours of such period or portion thereof.
(b) For cyclical or batch unit operations or unit processes, the total process weight for a period that covers a complete operation or an integral number of cycles, divided by the hours of actual process operation during such a period.
Where the nature of any process or operation or the design of any equipment is such as to permit more than one interpretation of this definition, the interpretation that results in the minimum value for allowable emission shall apply.
”Professional engineer” means a person licensed to practice professional engineering in the State of Delaware or otherwise eligible to practice engineering within the State as determined by the Delaware Association of Professional Engineers.
“Proportional sampling” means sampling at a rate that produces a constant ratio of sampling rate to stack gas flow rate.
“Publication rotogravure printing” means rotogravure printing upon paper which is subsequently formed into books, magazines, catalogues, brochures, directories, newspaper supplements and other types of printed materials.
“Reconstruction” means the replacement of components for an existing facility to such an extent that:
(1) The fixed capital cost of the new components exceeds 50 % of the fixed capital cost that would be required to construct a comparable entirely new facility, and
(2) It is technologically and economically feasible to meet the applicable standards set forth in this part.
“Recreational purposes” means any purpose which, in the judgment of the Department, fulfills a physical or social need, including, but not limited to, camping, ceremonies, and religious rites.
“Reference method” means any method specified in 7 DE Admin. Code 1120 for sampling and analyzing for an air pollutant.
“Refinery fuel gas” means any gas which is generated by a petroleum refinery process unit and which is combusted, including any gaseous mixture of natural gas and fuel gas.
“Refinery unit” means a set of components which are a part of a basic process operation, such as distillation, hydrotreating, cracking or reforming of hydrocarbons.
“Refuse” means garbage, rubbish, or trade waste.
“Reid vapor pressure” means the absolute pressure of a petroleum liquid product at 100oF (37.8oC) as measured by the standard test method set forth in 54 FR pp.11868‑11911.
“Removing”: As it applies to 7 DE Admin. Code 1121, removing means taking out friable asbestos materials used to insulate or fireproof any pipe, duct, boiler, tank, reactor, turbine, furnace, or structural member from any building, structure, facility or installation.
“Renovation”: As it applies to 7 DE Admin. Code 1121, the removing or stripping of friable asbestos material used to insulate or fireproof any boiler, tank, reactor, pipe, duct, turbine, furnace, or structural member. Operations in which load supporting structural members are wrecked or taken out are excluded.
“Ringlemann smoke chart” means the chart published and described in the U.S. Bureau of Mines Information Circular 8333, or any chart, recorder, indicator, or device for the measurement of smoke density which is approved by the Department as the equivalent of said Ringlemann Scale.
“Roadways” means surfaces on which motor vehicles travel including, but not limited to, highways, roads, streets, parking areas, and driveways.
“Roll coating” means the application of a coating material to a substrate by means of hard rubber or steel rolls.
“Rubbish” means waste solids or liquids including but not necessarily limited to, rags, clothes, leather, rubber, carpets, excelsior, paper, ashes, furniture, tin cans, glass, crockery, masonry, tires, or waste oil.
“Run” means the net period during which an emission sample is collected. Unless otherwise specified, a run may be either intermittent or continuous within the limits of good engineering practice.
“Salvage operation” means any business, trade or industry engaged entirely or partially in salvaging or reclaiming any product or material, including, but not necessarily limited to metal, chemicals, motor vehicles, shipping containers or drums.
“Sanitary landfill” means a method of disposing of refuse on land without creating nuisances or hazards to public health or safety by utilizing engineering principles to confine the refuse to the smallest practical area, to reduce it to the smallest volume, and to cover it with a layer of earth frequently as may be required by the permit.
“Scrubber” means a gas washer or auxiliary equipment designed to remove contaminants in wet form from products of combustion or from process emissions.
“Secondary ambient air quality standards” means those ambient air quality standards which, in the judgment of the Department, are requisite to protect the public welfare from any known or anticipated adverse effects associated with the presence of air contaminants in the ambient air.
“Secondary metal operation” means operations involving or related to the refining of metal when such operations use a raw material other than the metal ore.
“Secretary” means the Secretary of the Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control.
“Settleable particulates” means particulate matter present in air or other gases which end to settle out rather than remaining suspended.
“Silviculture” means the care and cultivation of forest trees.
“Six-minute period” means any one of the 10 equal parts of a one‑hour period.
“Sludge”: As it applies to 7 DE Admin. Code 1121, sludge means sludge produced by a treatment plant that processes municipal or industrial waste waters.
“Sludge dryer”: As it applies to 7 DE Admin. Code 1121, sludge dryer means a device used to reduce the moisture content of sludge by heating to temperatures about 65oC (ca. 150oF) directly with combustion gases.
“Small incinerator” means an incinerator which has a capacity equal to or less than 1000 pounds per hour.
“Smoke” means small gas‑borne particles resulting from incomplete combustion, consisting predominantly of carbon and other combustible material.
“Smoke detector” means a device using a light source and light detector which can automatically measure and record the light obscuring power of smoke at a specific location in the flue or stack.
“Solid fuel” means a fuel which is fired as a solid, such as anthracite or semi‑ anthracite, bituminous or sub‑bituminous coal, lignite, coke, wood, or any solid by‑product of a manufacturing process that may be substituted for any of the above specifically mentioned fuels.
“Solid waste” means refuse, more than 50 % of which is municipal type waste consisting of a mixture of paper, wood, yard wastes, food wastes, plastics, leather, rubber, and other combustibles and noncombustible materials such as glass and rock.
“Solvent” means organic materials which are liquid at standard conditions and which are used as dissolvers, viscosity reducers, or cleaning agents.
“Solvent metal cleaning” means the process of cleaning soils from metal surfaces by cold cleaning or open top vapor degreasing or conveyorized degreasing.
“Soot blowing” means the operation of removing soot, slag or fly ash from the firebox walls or the tubes of fuel burning equipment by the use of compressed air, steam or water.
“Splash filling” means the filling of a tank truck or stationary storage tank through a pipe or hose whose discharge opening is above the surface level of the liquid in the tank being filled.
“Stack” means a flue, chimney, conduit or other device constructed for the purpose of discharging air contaminants into the atmosphere.
“Stack height” means the vertical distance measured in feet between the point of discharge from a stack into the atmosphere and the land thereunder.
“Standard” means a standard of performance specified in 7 DE Admin. Code 1120.
“Standard conditions” means a gas temperature of 21oC (70oF) and a gas pressure of one atmosphere (14.7 pounds per square inch absolute).
“Stationary source” means any fixed building, structure, facility, installation, equipment or any motor vehicle, waterborne craft, aircraft or diesel locomotive deposited, parked, moored, or otherwise remaining temporarily in place, which emits or may emit any air contaminant.
“Stationary vessel” means any tank, reservoir, or container used for the storage of petroleum liquids, but does not include the following:
1. Pressure vessels which are designated to operate in excess of 15 pounds per square inch gauge without emissions to the atmosphere except under emergency conditions.
2. Subsurface caverns or porous rock reservoirs.
3. Underground tanks if the total volume of petroleum liquids added to and taken from a tank annually does not exceed twice the volume of the tank.
“Stripping” : As applies to 7 DE Admin. Code 1121, stripping means taking off friable asbestos material used for insulation or fire‑proofing from any pipe, duct, boiler, tank, reactor, turbine, furnace, or structural member.
“Submerged filling” means filling of a tank truck or stationary tank through a pipe or hose whose discharge opening is entirely submerged when the liquid level is six inches above the bottom of the tank.
“Sulfuric acid plant” means any facility producing sulfuric acid by the contact process of burning elemental sulfur, alkylation acid, hydrogen sulfide, organic sulfides and mercaptans, or acid sludge, but does not include facilities where conversion to sulfuric acid is utilized primarily as a means of preventing emissions to the atmosphere of sulfur dioxide or other sulfur compounds.
“Sulfur recovery operation” means any operation designed for the recovery of elemental sulfur, including any upstream part of the operation designed to separate hydrogen sulfide from refinery gases or water.
“Surfacer coating” means the surfacer coatings applied over the primer and beneath the topcoat.
“Suspended particulates” means particulate matter which remains suspended in ambient air.
“Tail gases” means gases and vapors released into the atmosphere from an industrial process after all reaction and treatment has taken place.
“Topcoat” means the surface coatings applied for the purpose of establishing the color or protective surface, including groundcoat and paint sealer materials.
“Trade waste” means any solid, liquid, or gaseous waste material or rubbish resulting from construction, land clearing for construction or development, building operations, or the prosecution of any business, trade, or industry including, but not necessarily limited to, plastic products, cartons, paint, grease, oil and other petroleum products, chemicals or cinders.
“True vapor pressure” means the equilibrium partial pressure exerted by petroleum liquid as determined in accordance with methods described in American Petroleum Institute Bulletin 2517, Evaporation Loss from Floating Roof Tanks, 1962.
“Turnaround” means the procedure of shutting a refinery unit down after a run to do necessary maintenance and repair work and putting the unit back on stream.
“Unsafe-to-monitor valve” means any valve which the facility operator has demonstrated cannot be monitored without exposing monitoring personnel to an immediate danger.
“Vacuum producing system” means any reciprocating, rotary, or centrifugal blower or compressor, or any jet ejector or device that takes suction from a pressure below atmospheric and discharges against atmospheric pressure.
“Valves not externally regulated” means valves that have no external controls, such as in‑line check valves.
“Vapor balance system” means VAPOR BALANCE SYSTEM: a combination of pipes or hoses which create a closed system between the vapor spaces of an unloading tank and a receiving tank such that vapors displaced from the receiving tank are transferred to the tank being unloaded.
“Vapor-laden delivery vessel” means any delivery vessel containing any organic vapors displaced from a stationary vessel during loading of such vessel.
“Vapor-laden stationary vessel” means any stationary vessel containing any organic vapors displaced from delivery vessel during loading of such vessel.
“Vapor recovery system” means a vapor gathering system capable of collecting all hydrocarbon vapors and gases discharged from the storage vessel and a vapor disposal system capable of processing such hydrocarbon vapors and gases so as to prevent their emission to the atmosphere (applicable to 7 DE Admin. Code 1120).
“Vapor recovery system” means a system that prevents release to the atmosphere of no less than 90% by weight of organic compounds emitted during the operation of any transfer, storage, or process equipment (Applicable to 7 DE Admin. Code 1124).
“Vapor tight” means capable of holding an initial positive pressure of 18 inches of water column and a vacuum pressure of six inches of water column without a pressure change of more than three inches of water column in five minutes.
“Vents”: See “Stack”.
“Vinyl coating” means applying a decorative or protective topcoat, or printing on vinyl coated fabric or vinyl sheets.
“Visible emissions” means any air contaminant.
“Visibility meter” means any device used for the purpose of measuring, recording, or indicating the reflectance or opacity to light of an air contaminant stream.
“Volatile organic compounds” (Also denoted as VOCs) means any carbon-containing compound, excluding carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbonic acid, metallic carbides or carbonates, and ammonium carbonate, which participates in atmospheric photochemical reactions. This includes any such organic compound other than the following, which have been determined to have negligible photochemical reactivity:
* t-butyl acetate is a VOC for purposes of all recordkeeping, emissions reporting, photo-chemical dispersion modeling and inventory requirements which apply to VOC and shall be uniquely identified in emission reports, but is not a VOC for purposes of VOC emissions limitations or VOC content requirements.
“Waste oil” means used or spent oil or solvents or other volatile hydrocarbons, including but not limited to crankcase oil.
“Wastewater separator” means any device or piece of equipment which utilizes the difference in density between oil and water to recover oil. It does not include any secondary separator located downstream from a primary separator, nor any wastewater treatment units such as a flocculator, clarifier or aerator.
“Weak nitric acid” means nitric acid which is 30% to 70% in strength.
02/01/1981
3.1 In certain regulations, air quality standards will be established. These standards shall not be interpreted to allow significant deterioration of existing air quality in any portion of the State; otherwise; they shall be paramount in matters pertaining to the control of air pollution throughout the State.
3.2 In addition to or supplemental to these air quality standards, certain emission requirements will be specified. Such emission requirements are selected as minimum controls necessary to ensure a reasonable quality of air throughout the State. Where it is established that these emission requirements are inadequate to attain or maintain the applicable air quality standard, the Department shall exercise its authority to require additional control measures.
3.3 The Department intends to have regulations adopted governing the control of air pollution as rapidly as practicable. The lack of Regulation governing an air contaminant or combination of air contaminants will not prevent the Department from taking any and all actions necessary to maintain a reasonable quality of air throughout the State.
3.4 If any part of these regulations, or the application of any part thereof, is held invalid or unconstitutional, the application of such part to other persons or circumstances, and the remainder of these Regulations shall not be affected thereby and shall be deemed valid and effective.
3.5 The Department may enter into agreement or agreements on a regional basis for the purpose of attaining air quality goals. Such interstate agreements shall facilitate the attainment and maintenance of air quality standards.
02/01/1981
The abbreviations used in these regulations have the following meanings:
*NOTE: This abbreviation is actually µg. but may not have been converted to this symbol throughout all regulations.







